Transfer Formats
Different data transfer formats exist because a generic format is required to represent all the different aspects (GG XML), and the recipients are using more specific formats, often designed to represent only some aspects of the data: Darwin Core Archive (DwC-A) for the import for GBIF, TaxPub/JATS XML for SIBiLS, or JSON/XHTML to export data to BLR/Zenodo.
Figure 1: Overview of the data flow between literature based data and the data domains in BKH (specimens, taxonomic names, and sequences). The Data Transfer Formats are indicated in the graph.
The respective files are produced in real time and readily available, or a recipient system such as GBIF is notified of updates and it harvests the data later.
Darwin Core Archive (DwC-A):
- Purpose: Used for sharing biodiversity data, especially catalog data based on Darwin Core terms and guidelines.
- Description: A simple and extensible arrangement of tabular data in a star schema. Commonly used for data import to GBIF.
TaxPub XML (Treatment):
- Purpose: Used for importing treatments into SIBiLS.
- Description: Based on JATS TaxPub, it allows the transfer of treatment data. Annotations from SIBiLS are copied into EuropePMC via the SciLite gateway.
JSON / XHTML (Treatment, Figures):
- Purpose: Used for interaction with Zenodo.
- Description: JSON format is used for Zenodo interactions, while XHTML is used for taxonomic treatments as the digital objects required to create Zenodo deposits.
GG XML (Treatment):
- Purpose: Used as Plazi's internal XML format for storing treatments in TreatmentBank.
- Description: Represents all significant features and structures of treatments, including nomenclature acts, treatment citations, materials citations, and more. It serves as the basis for transformations into other formats.
Figure 2 presents a simple graphical representation of the relationships between these formats:
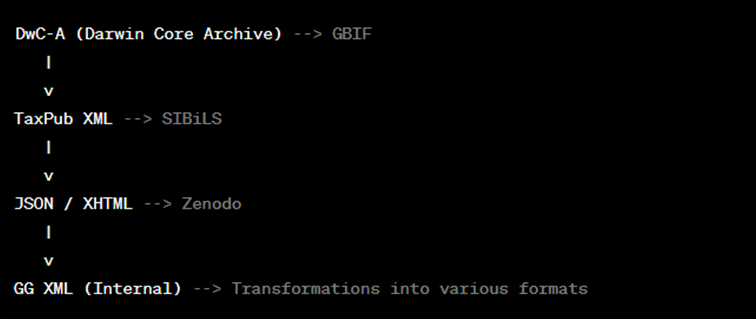
Figure 2. This representation shows the flow of data from the generic GG XML format to specific formats used by different recipients and systems. The formats serve various purposes, such as data sharing, import, and interaction with platforms like GBIF, SIBiLS, and Zenodo. The GG XML format acts as the central format from which data is transformed into other formats as needed.
