The PlutoF platform has been designed for storing and managing biodiversity data over the web. PlutoF provides database and computing services for taxonomical, ecological, phylogenetical, etc. research. The purpose of the platform is to provide synergy through common modules for the classifications, taxon names, analytical tools, etc. In addition to storing diverse biodiversity data, various supporting services are accessible in all modules (Figure 1).
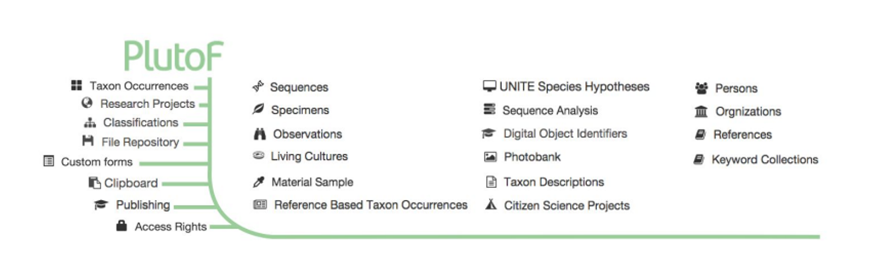 |
Figure 1. Supporting services and modules of PlutoF. Base services (on the left) are accessible in all modules. |
|---|
Here are some key features and services offered by PlutoF:
-
Data Management Plan: This includes guidelines on collecting, managing, and storing data during a research project.
-
Creation of Datasets: Users can create datasets in PlutoF by importing data from CSV files, manually entering data on the online workbench, or using the mobile application PlutoF GO for quick and easy data entry.
-
Curating and Sharing Datasets: The platform allows collaboration with other scientists, students, and citizen scientists by sharing individual records or entire projects and datasets.
-
Machine Readable Data: PlutoF provides public web services for retrieving data in a machine-readable format.
-
Running Analyses: The platform features an analysis module providing analytical services for molecular sequence identification and species discovery from environmental DNA (eDNA) samples.
-
DOI Publishing: Users can request a Digital Object Identifier (DOI) for their dataset or publish the data in the global data portal GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility).
-
Managing Different Data Types: This includes specimens, traits, samples, DNA sequences, eDNA, observations, taxa and classifications, references, and multimedia.
-
Target Audience: The platform is designed for researchers, data managers, citizen scientists, labs, organizations, museums, and universities.
PlutoF is a comprehensive tool for those involved in biodiversity research and data management, offering a wide array of functionalities to support the full lifecycle of biological data management and publication.
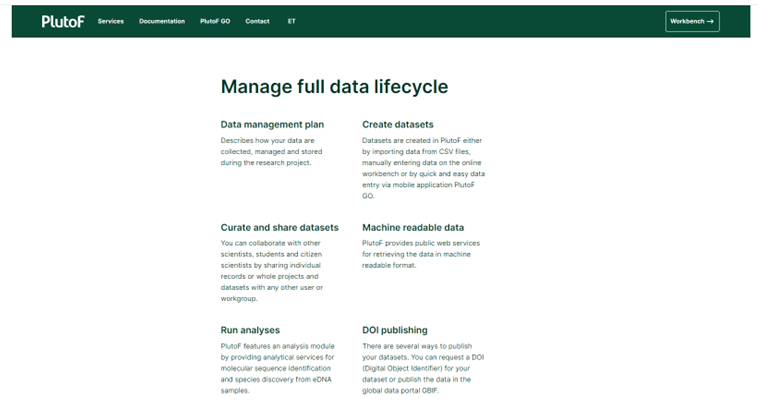 |
Figure 2. PlutoF offered Services |
|---|
PlutoF service is rather simple to use for non-expert users. Here is a practical use case of the service for a citizens' science project.
Citizen scientists can effectively use the PlutoF platform in various ways, contributing to biodiversity research
and data collection. Here's a detailed and practical example of how citizen scientists might engage with the
PlutoF service:
Project: Urban Biodiversity Monitoring
Objective:
To monitor and record the biodiversity in an urban area, focusing on bird species.
Steps for Citizen Scientists:
- Citizen scientists register on the PlutoF platform.
- They undergo a brief online training module available on PlutoF, learning how to identify local bird species and how to record observations accurately.
2. Using PlutoF GO Mobile App:
- Participants download the PlutoF GO mobile app, which is designed for easy data entry in the field.
- The app allows them to log observations directly, including date, time, location (using GPS), and species observed.
3. Observation and Data Collection:
- Participants go to various locations within the urban area - parks, gardens, streets - to observe birds.
- They use the PlutoF GO app to record each sighting, adding notes on the bird's behavior, the number of individuals seen, and any unique characteristics.
- The app allows uploading photos or audio recordings, which can be particularly useful for verifying species.
4. Data Curation and Sharing:
- The data collected by each participant is uploaded to the PlutoF cloud, where it is stored securely.
- Participants can choose to share their observations with the broader PlutoF community or keep them private for specific projects.
5. Community Engagement and Collaboration:
- Citizen scientists can view and comment on each other's observations, fostering a community of practice and learning.
- They can join forums or groups within PlutoF focused on specific aspects of urban biodiversity or bird watching.
6. Data Analysis and Visualization:
- PlutoF provides tools for analyzing the collected data. Participants can view maps of species distribution, frequency charts, and other visual data representations.
- These analyses can help identify patterns, such as the prevalence of certain species in specific areas or changes in populations over time.
7. Contribution to Research and Conservation:
- The aggregated data from all participants can be made available to professional researchers and conservationists.
- This data helps in understanding urban biodiversity, informing conservation strategies, and possibly influencing urban planning to be more wildlife-friendly.
8. Feedback and Learning:
- Participants receive feedback on their contributions, including confirmations of species identifications and insights from expels.
- They have access to educational resources on PlutoF, enhancing their knowledge about biodiversity and conservation.
Outcome:
Through this project, citizen scientists not only contribute valuable data to biodiversity research but also gain a deeper understanding and appreciation of the wildlife in their urban environment. The PlutoF platform facilitates the entire process, from data collection to analysis, making it accessible and engaging for individuals without a formal background in science.